Fat v/s Muscle
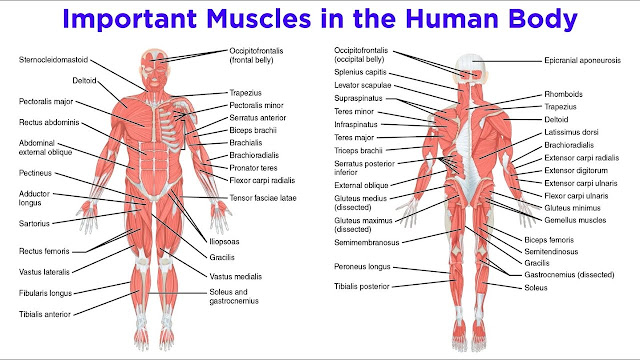
There are about 600 muscles in the human body. The three main types of muscle include skeletal, smooth and cardiac. The brain, nerves and skeletal muscles work together to cause movement – this is collectively known as the neuromuscular system. Different types of muscle The three main types of muscle include: Skeletal muscle – the specialised tissue that is attached to bones and allows movement. Together, skeletal muscles and bones are called the musculoskeletal system (also known as the locomotor system). Generally speaking, skeletal muscle is grouped into opposing pairs such as the biceps and triceps on the front and back of the upper arm. Skeletal muscles are under our conscious control, which is why they are also known as voluntary muscles. Another term is striated muscles, since the tissue looks striped when viewed under a microscope. Smooth muscle – located in various internal structures including the digestive tract, uterus and blood vessels such as arteries. S...

